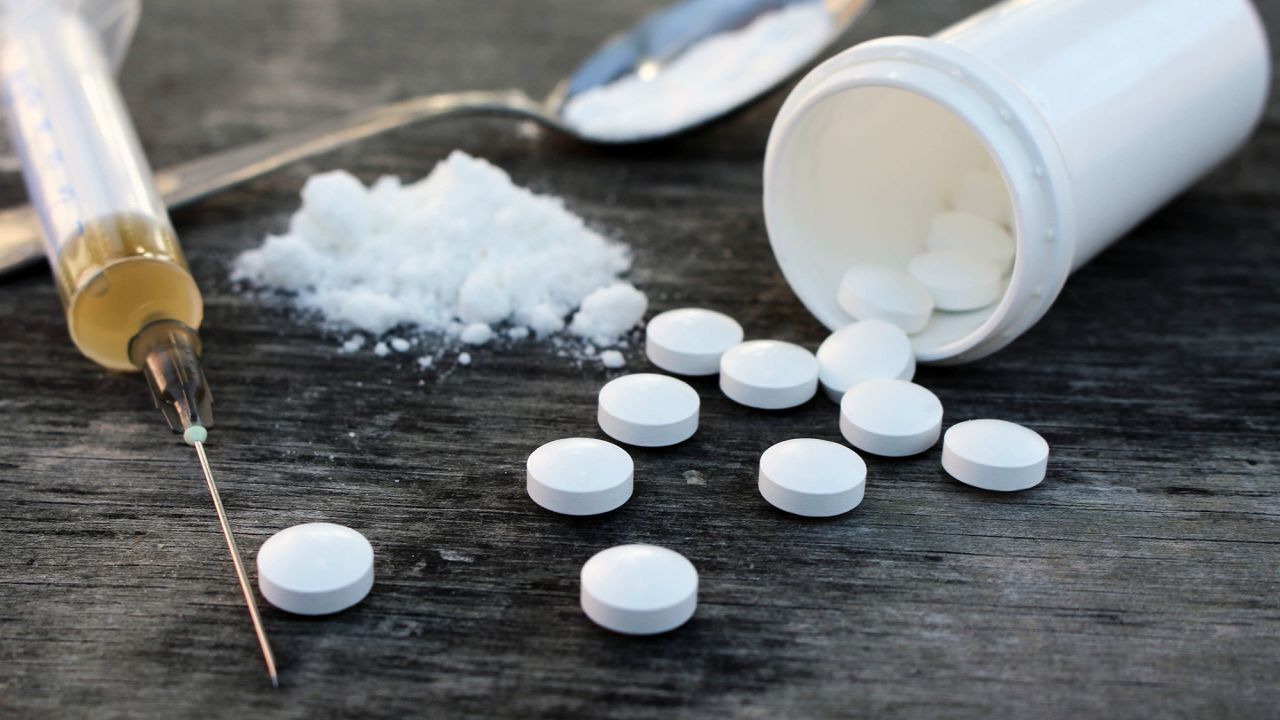
The opioid crisis has become a significant public health issue affecting millions worldwide. This crisis involves the widespread misuse of both prescription and non-prescription opioids, leading to addiction, overdose, and death. Opioids include drugs like oxycodone, fentanyl, and heroin. The crisis began in the late 1990s when pharmaceutical companies reassured the medical community that patients would not become addicted to prescription opioid pain relievers. Doctors started prescribing them at greater rates, which led to widespread misuse before it became clear that these medications could indeed be highly addictive. Understanding the facts about the opioid crisis is crucial for raising awareness and finding solutions to combat this epidemic. Here are 20 essential facts to help you grasp the magnitude and impact of this ongoing issue.
Understanding the Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis is a severe public health issue affecting millions worldwide. It's essential to grasp the scope and impact of this crisis to address it effectively.
- Opioids are a class of drugs that include prescription pain relievers, heroin, and synthetic opioids like fentanyl.
- The crisis began in the late 1990s when pharmaceutical companies reassured the medical community that patients would not become addicted to prescription opioid pain relievers.
- Over 130 people in the United States die every day from opioid overdoses.
- The misuse of and addiction to opioids—including prescription pain relievers, heroin, and synthetic opioids such as fentanyl—is a serious national crisis that affects public health as well as social and economic welfare.
The Impact on Public Health
The opioid crisis has far-reaching consequences on public health, affecting individuals, families, and communities.
- Opioid addiction can lead to severe health issues, including respiratory depression, increased risk of infectious diseases, and mental health disorders.
- Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) is a condition in which a baby is born dependent on opioids due to the mother's use during pregnancy.
- The spread of infectious diseases like HIV and hepatitis C has been linked to opioid misuse, particularly through needle sharing.
- Emergency room visits for opioid overdoses have increased significantly, putting a strain on healthcare systems.
Economic and Social Consequences
Beyond health, the opioid crisis has significant economic and social repercussions.
- The economic burden of the opioid crisis in the U.S. is estimated to be over $78 billion annually, including healthcare costs, lost productivity, addiction treatment, and criminal justice involvement.
- Families are often torn apart by opioid addiction, leading to increased rates of child neglect and foster care placements.
- Communities face increased crime rates and homelessness due to the widespread impact of opioid addiction.
- Employers report higher absenteeism, reduced productivity, and increased healthcare costs due to opioid misuse among employees.
Efforts to Combat the Crisis
Various strategies are being implemented to address and mitigate the opioid crisis.
- Prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) are being used to track and monitor opioid prescriptions to prevent misuse.
- Increased access to addiction treatment services, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT), is crucial in helping individuals recover from opioid addiction.
- Naloxone, a medication that can rapidly reverse an opioid overdose, is being made more widely available to first responders and the public.
- Public awareness campaigns aim to educate people about the dangers of opioid misuse and the importance of proper medication disposal.
The Role of Policy and Legislation
Government policies and legislation play a critical role in addressing the opioid crisis.
- The SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act, passed in 2018, is a comprehensive law aimed at combating the opioid epidemic through various measures, including expanding treatment options and improving access to care.
- States have implemented prescription drug take-back programs to safely dispose of unused medications and prevent them from being misused.
- Some states have enacted laws to limit the quantity of opioids that can be prescribed, aiming to reduce the risk of addiction and overdose.
- Federal funding has been allocated to support research on pain management alternatives and the development of non-addictive pain medications.
Understanding the Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis is a complex issue affecting millions. It's not just about addiction; it's about the social, economic, and health impacts that ripple through communities. Prescription practices, illegal drug trade, and mental health all play roles in this epidemic. Solutions require a multi-faceted approach, including education, treatment programs, and policy changes.
Awareness is key. Knowing the facts helps in making informed decisions and supporting those affected. Communities must come together to combat this crisis, offering support and resources to those in need.
By staying informed and proactive, we can make strides in reducing the impact of opioids. Every small effort counts in creating a safer, healthier environment for everyone. Let's continue to educate ourselves and others, pushing for change and offering hope to those struggling.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.