Heat waves can be intense and sometimes dangerous, but they also hold some fascinating facts. Did you know that heat waves are the deadliest weather phenomenon in the United States? They cause more fatalities than hurricanes, tornadoes, or floods. Heat waves can also affect infrastructure, causing roads to buckle and train tracks to warp. Plants and animals struggle too, with crops failing and wildlife seeking cooler areas. Cities often experience the urban heat island effect, making them even hotter. Understanding these facts can help you stay safe and appreciate the power of nature. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 50 intriguing facts about heat waves!
What is a Heat Wave?
A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity. These extreme weather events can have significant impacts on health, infrastructure, and the environment.
- A heat wave is typically defined as a period of at least three consecutive days with temperatures above a certain threshold.
- The exact temperature threshold for a heat wave varies by region, depending on the local climate.
- Heat waves are more common in urban areas due to the "urban heat island" effect, where concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat.
- They can occur in both summer and winter, though summer heat waves are more common.
- Heat waves can exacerbate drought conditions by increasing evaporation rates.
Historical Heat Waves
Throughout history, heat waves have caused significant disruptions and even fatalities. Here are some notable examples:
- The European heat wave of 2003 resulted in over 70,000 deaths, making it one of the deadliest in recorded history.
- In 2010, Russia experienced a severe heat wave that led to wildfires and the death of approximately 56,000 people.
- The 1995 Chicago heat wave caused over 700 deaths, primarily among the elderly and those without air conditioning.
- Australia's 2009 heat wave led to the "Black Saturday" bushfires, which killed 173 people.
- The 2015 Indian heat wave saw temperatures soar above 47°C (116.6°F), resulting in over 2,500 deaths.
Health Impacts of Heat Waves
Heat waves can have serious health consequences, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
- Heat exhaustion and heat stroke are common during heat waves, with symptoms including dizziness, nausea, and confusion.
- Dehydration is a significant risk, as high temperatures increase the body's need for water.
- Chronic conditions like heart disease and respiratory illnesses can be exacerbated by extreme heat.
- Heat waves can lead to an increase in hospital admissions and emergency room visits.
- Mental health can also be affected, with studies showing a rise in anxiety and depression during prolonged heat events.
Environmental Effects of Heat Waves
The environment also suffers during heat waves, with various ecosystems and species being impacted.
- Heat waves can cause significant stress to plants, leading to reduced crop yields and food shortages.
- Wildfires are more likely to occur during heat waves due to dry conditions and high temperatures.
- Aquatic ecosystems can be affected, as higher water temperatures reduce oxygen levels, harming fish and other marine life.
- Urban areas may experience increased air pollution, as heat can cause chemical reactions that produce smog.
- Prolonged heat can lead to soil degradation and desertification in vulnerable regions.
Economic Consequences of Heat Waves
The economic impact of heat waves can be substantial, affecting various sectors and leading to significant financial losses.
- Agriculture is often hit hard, with heat waves causing crop failures and livestock deaths.
- Energy demand spikes during heat waves, leading to higher electricity costs and potential blackouts.
- Infrastructure can be damaged, with roads and railways buckling under extreme temperatures.
- Tourism may decline, as people avoid traveling to areas experiencing heat waves.
- Businesses may face increased costs for cooling and employee health care.
How to Stay Safe During a Heat Wave
Taking precautions during a heat wave is essential to protect yourself and others from the dangers of extreme heat.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and avoiding alcohol and caffeine.
- Wear lightweight, loose-fitting clothing to help your body stay cool.
- Avoid strenuous activities during the hottest parts of the day, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use fans and air conditioning to keep indoor spaces cool.
- Check on vulnerable individuals, such as the elderly and those with health conditions, to ensure they are safe.
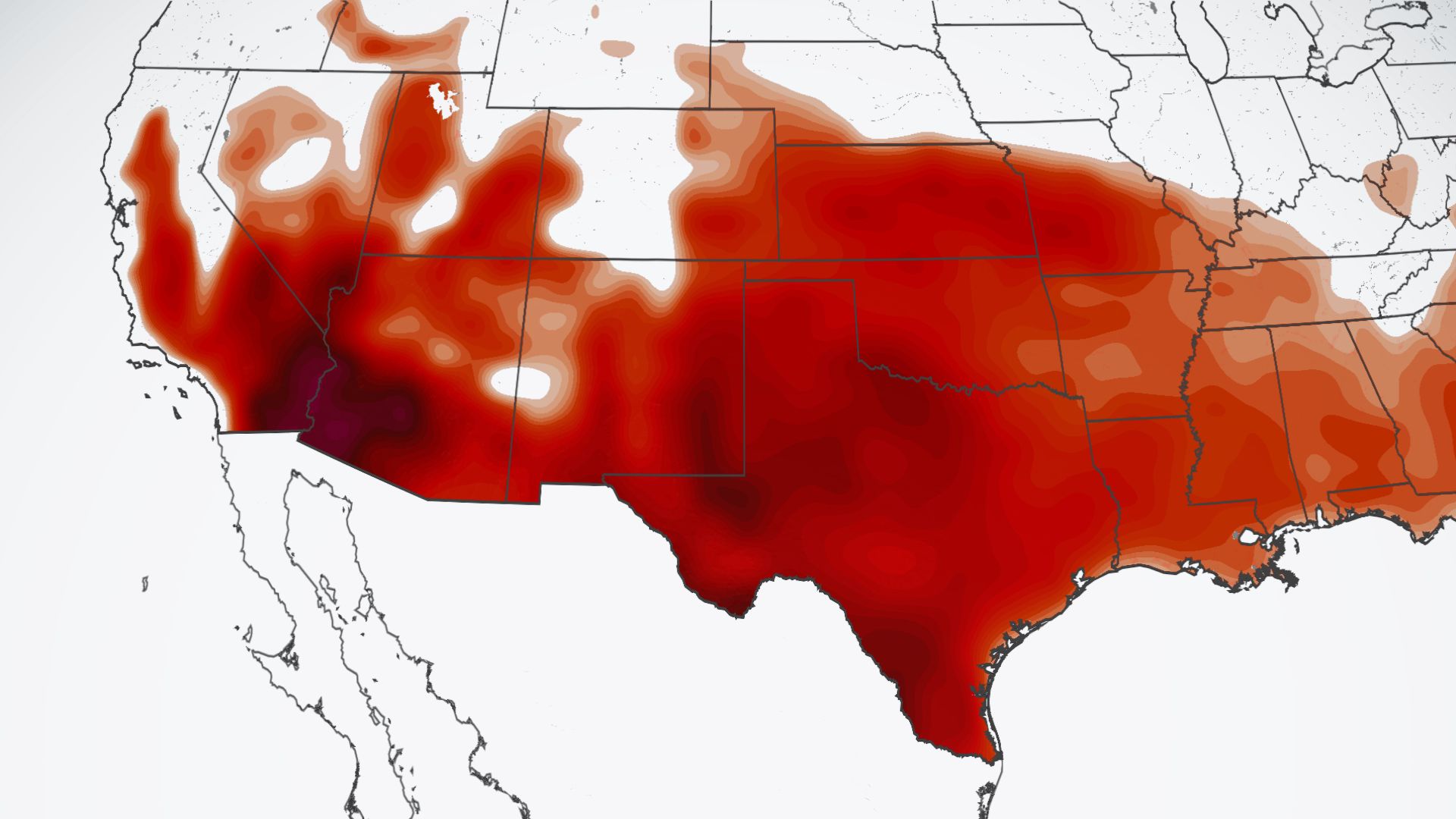
Climate Change and Heat Waves
Climate change is expected to increase the frequency and intensity of heat waves, making them a growing concern for the future.
- Global warming is causing average temperatures to rise, leading to more frequent heat waves.
- Heat waves are becoming longer, with some lasting weeks instead of days.
- The intensity of heat waves is increasing, with record-breaking temperatures becoming more common.
- Urbanization and deforestation contribute to the severity of heat waves by reducing natural cooling mechanisms.
- Mitigating climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to preventing more extreme heat waves.
Interesting Facts About Heat Waves
Here are some lesser-known facts about heat waves that highlight their complexity and impact.
- The term "heat wave" was first used in the United States in the 1890s.
- Heat waves can cause "heat islands" in cities, where temperatures are significantly higher than in surrounding rural areas.
- Some animals, like bats, are particularly vulnerable to heat waves and can die in large numbers during extreme heat events.
- Heat waves can affect sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and other sleep disorders.
- The color of your clothing can impact how hot you feel; lighter colors reflect heat, while darker colors absorb it.
Preparing for Future Heat Waves
As heat waves become more common, it's important to be prepared and take steps to mitigate their impact.
- Planting trees and creating green spaces in urban areas can help reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Building materials that reflect heat, such as cool roofs, can keep buildings cooler.
- Early warning systems can alert people to impending heat waves, allowing them to take precautions.
- Public education campaigns can raise awareness about the dangers of heat waves and how to stay safe.
- Investing in renewable energy sources can help reduce the greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change.
Global Efforts to Combat Heat Waves
Countries around the world are taking steps to address the challenges posed by heat waves.
- France implemented a heat wave action plan after the deadly 2003 heat wave, which includes public cooling centers and emergency response measures.
- India has developed heat action plans for several cities, focusing on public awareness and infrastructure improvements.
- Australia has introduced building codes that require new homes to be designed to withstand extreme heat.
- The United States has established the National Integrated Heat Health Information System to coordinate efforts to address heat waves.
- The World Health Organization provides guidelines and resources to help countries prepare for and respond to heat waves.
The Heat Wave Rundown
Heat waves aren't just about high temperatures. They impact health, agriculture, and even the economy. Knowing the signs and staying prepared can save lives. Simple steps like staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat, and checking on vulnerable neighbors make a big difference.
Heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change. This makes it crucial to understand their effects and how to mitigate them. Urban areas often suffer more due to the "urban heat island" effect, where concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat.
Remember, heat waves can happen anywhere, not just in traditionally hot regions. Stay informed, stay safe, and take proactive measures to protect yourself and your community. By doing so, we can better handle these extreme weather events and reduce their impact on our daily lives.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.