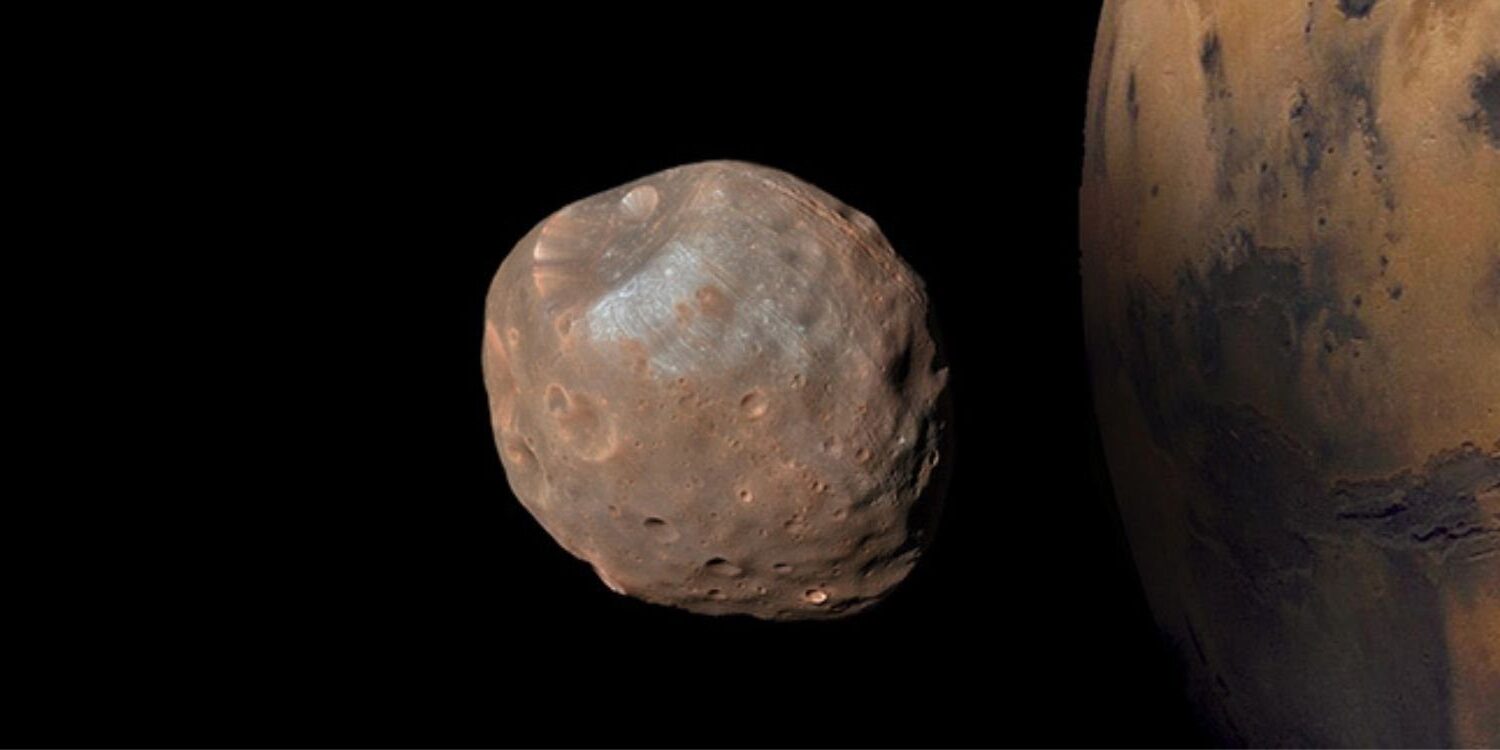
Deimos, one of Mars' two moons, often gets overshadowed by its larger sibling, Phobos. But this tiny celestial body holds many intriguing secrets. Did you know Deimos is only about 12.4 kilometers in diameter? That's smaller than many cities on Earth! Unlike our Moon, Deimos has a smoother surface, thanks to a thick layer of dust that fills its craters. Scientists believe Deimos might be a captured asteroid from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Its slow drift away from Mars hints at a mysterious past. Ready to learn more about this fascinating moon? Let's dive into 12 amazing facts about Deimos!
What is Deimos?
Deimos is one of Mars' two moons. Smaller and less famous than its sibling Phobos, Deimos has its own unique characteristics. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this tiny celestial body.
-
Deimos is tiny. Deimos measures only about 12.4 kilometers (7.7 miles) in diameter. This makes it one of the smallest moons in our solar system.
-
Deimos has an irregular shape. Unlike Earth's moon, Deimos isn't round. Its shape is more like a lumpy potato due to its weak gravity, which can't pull it into a sphere.
-
Deimos orbits Mars. Deimos takes about 30.3 hours to complete one orbit around Mars. This is much slower compared to Phobos, which orbits Mars in just 7.7 hours.
How was Deimos Discovered?
Deimos was discovered in the late 19th century. Its discovery added to our understanding of Mars and its natural satellites.
-
Deimos was discovered in 1877. American astronomer Asaph Hall discovered Deimos on August 12, 1877, just six days before he discovered Phobos.
-
Named after a Greek god. Deimos is named after the Greek god of terror, who was a son of Ares (Mars) and Aphrodite (Venus). This naming follows the tradition of naming celestial bodies after mythological figures.
-
Discovered using a telescope. Hall used the United States Naval Observatory's 26-inch refractor telescope, the largest of its kind at the time, to find Deimos.
What is Deimos Made Of?
Understanding the composition of Deimos helps scientists learn more about the formation of moons and planets.
-
Deimos is made of rock and ice. Like many other moons in the solar system, Deimos is composed mainly of carbon-rich rock and ice. This composition is similar to that of asteroids in the outer solar system.
-
Surface covered in dust and loose rocks. Deimos' surface is covered with a thick layer of regolith, which is a mix of dust and loose rocks. This gives it a smooth appearance compared to Phobos.
-
Few craters on Deimos. Deimos has fewer craters than Phobos. The largest crater on Deimos, named Swift, is about 3 kilometers (1.9 miles) in diameter.
How Does Deimos Compare to Phobos?
Deimos and Phobos are often compared due to their proximity and relationship with Mars. However, they have distinct differences.
-
Deimos is farther from Mars. Deimos orbits Mars at a distance of about 23,460 kilometers (14,580 miles), which is much farther than Phobos' orbit of about 6,000 kilometers (3,700 miles).
-
Deimos has a smoother surface. Compared to Phobos, Deimos has a smoother surface with fewer large craters. This is likely due to a thicker layer of regolith that covers its surface.
-
Deimos is less massive. Deimos has a mass of about 1.48 x 10^15 kilograms, which is significantly less than Phobos' mass of about 1.08 x 10^16 kilograms.
Final Glimpse at Deimos
Deimos, Mars' smaller moon, holds many intriguing facts. Its small size and irregular shape make it unique among celestial bodies. Unlike our moon, Deimos has a smooth surface with fewer craters, suggesting a different history. Its low gravity means any loose material tends to drift away, creating a dusty surface. Deimos orbits Mars every 30 hours, making it a swift traveler in the Martian sky.
Scientists believe Deimos might be a captured asteroid, adding to its mystery. Its composition of carbon-rich rock and ice hints at its origins. Despite its small size, Deimos plays a significant role in our understanding of Mars and its moons. As we continue to explore space, Deimos remains a fascinating subject for study, offering clues about the formation and evolution of our solar system.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.